It is important to acknowledge that whatever we ingest becomes part of our bodies, either temporarily or permanently. Thus, food has a direct impact on all parts of our body, including the eyes. Numerous research studies are currently looking at nutrition and its effect on eye health, which is often evident. [For instance, the optometrist can clearly see the effects of heart disease and diabetes on eye health as the equipment can clearly show fatty deposits in the smallest of the blood vessels of the eye and this, in turn, is a direct reflection of one’s diet]. So what can food do for our eyesight?
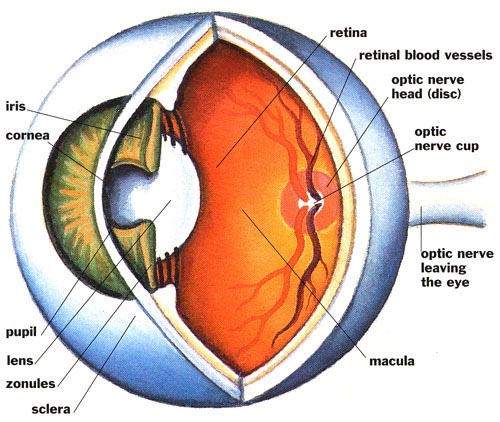
The two leading causes of vision loss in Canada are Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD) and Cataracts. AMD destroys the macula of the eye, which is responsible for central vision and visual acuity, needed for reading, identifying faces, driving, etc. Cataract is another common condition in which the lens of the eye becomes cloudy, causing blurry vision. Several vitamins and minerals that are part of the eye structure or function have shown promise of fending off these conditions.
Nutrients that Protect Your Eyes
Vitamins A, C, and E
These nutrients are antioxidants, which means, they protect your body from cell damage that occurs as a natural part of aging. Thus, these vitamins may have the ability to slow down or prevent the progression of age-related eye disease. Further more, vitamin A helps the retina to function properly, making it important in preventing night blindness. Vitamin C, aside from being an antioxidant, is also a component of they lens of the eye. Studies show that vitamins A, C and E may help prevent the clouding of the lens (that is cataracts) as they make up part of the eye structure and prevent cell damage. Vitamin A has also been shown to lower risk of AMD.
Lutein and Zeaxanthin
These are carotenoids- yellow and red plant pigments that are essential components of eye lens and the macular pigment of the retina. They protect the eye by acting as powerful antioxidants and by filtering high-energy blue light that may cause eye damage. Both of these have also been suggested to help prevent cataracts and AMD.
Zinc and Selenium
These mineral helps your body to absorb all the above mentioned antioxidants, which in turn help prevent eye disease among many other things.
Omega-3 Fats
These fatty acids, usually found in fatty fish, are components of the central nervous system as well as the retina of the eye. Consuming fish along with other omega-3 rich foods may protect our eyes from AMD. Furthermore, omega-3 fats possess anti-inflammatory properties, which may have a protective effect not only on the eyes, but also the heart among other organs.
So the final question is: where do you find all these nutrients?…
NUTRIENT |
SIGNIFICANT FOOD SOURCES |
VITAMIN A |
1 cup of mango or cantaloupe |
VITAMIN C |
Practically all fruit and vegetables are a sources of vitamin C, richest sources are: |
VITAMIN E |
-1oz of almonds, hazelnuts, sunflower seeds |
ZINC |
-3oz of oysters, beef, Alaska crab, chicken (dark meat) |
SELENIUM |
-3oz of light canned tuna, cod, turkey |
LUTEIN & ZEAXANTHIN |
-1/2 cup cooked kale, spinach, Swiss chard, collard greens, turnip greens, broccoli |
OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS |
-2.5 to 3.0 oz of salmon, trout, canned sardines, cooked mackerel, canned anchovies, arctic char |
*Note: in many cases cooked foods offer higher amounts of certain nutrients than raw.
To summarize, one can see a recurring pattern in these food lists: load up on bright-coloured fruits and vegetables, especially cooked dark leafy greens, and ensure to have fatty fish 2 to3 times per week. Consuming adequate servings of fruits and veggies along with the fish, does not only help your eyes but helps prevent and manage many other chronic conditions like Diabetes and heart disease.
